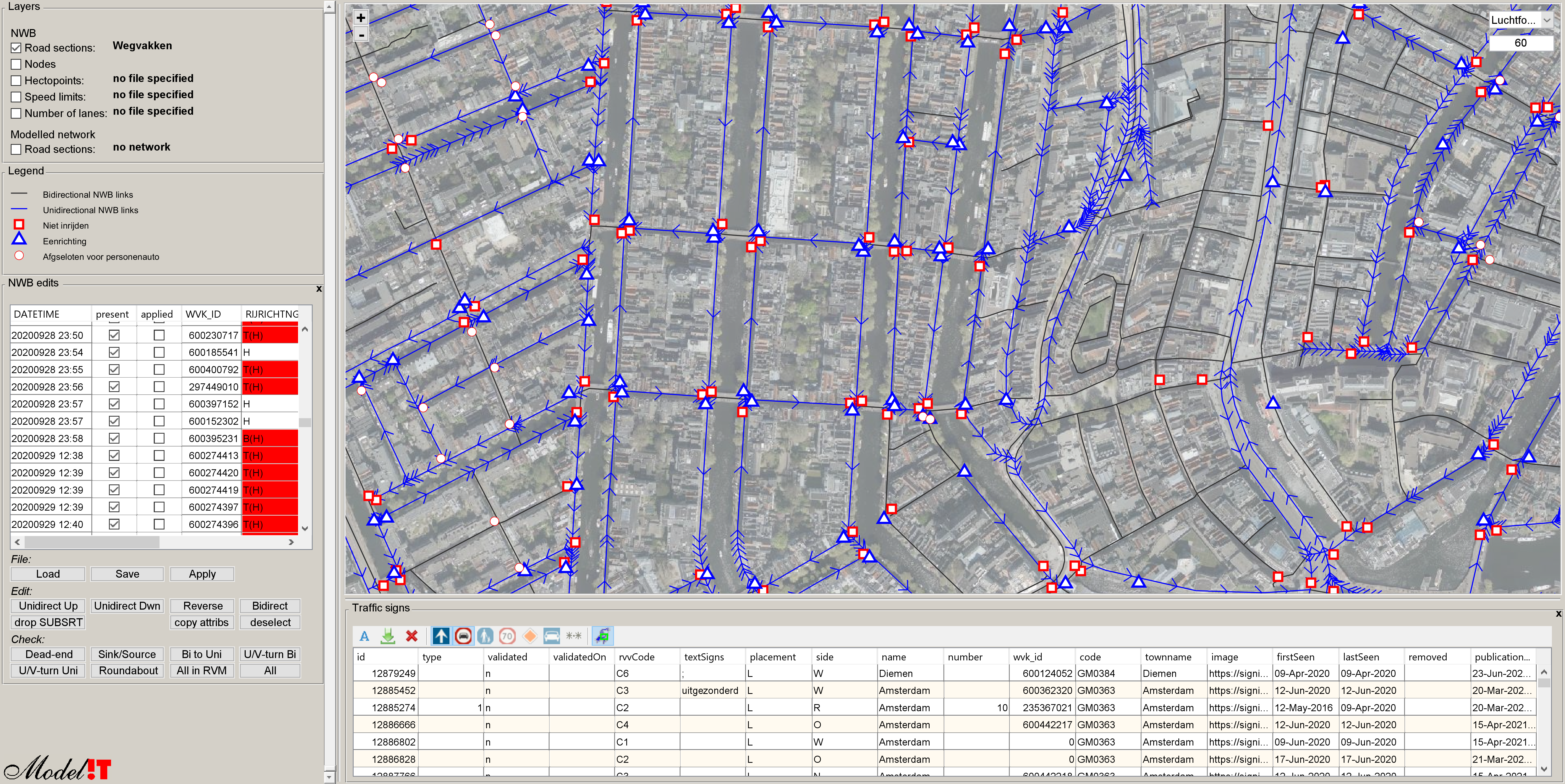
The Dutch Road Authorities together with local authorities maintain a database of all public traffic signs in the Netherlands. For each sign the exact location, categorial code, and photo image is stored.
Traffic signs make up a valuable source of information when constructing a traffic model. They provide additional context to the graph that represents a transport network and allow random checks when verifying a model configuration.
The following type of signs are of particular interest:
- signs that indicate oneway traffic
- signs for priority roads and right of way
- maximum speed
- (partial) road closures
- access restricted to pedestrians or cyclists
A plugin has been created for TRIP that supports the following:
- Automatic retrieval of the latest version of the database
- Plotting the traffic sign locations on the map
- Table presentation of the traffic sign data
- Select options for traffic signs using categories or spatial constraints
- Drill down to photo image
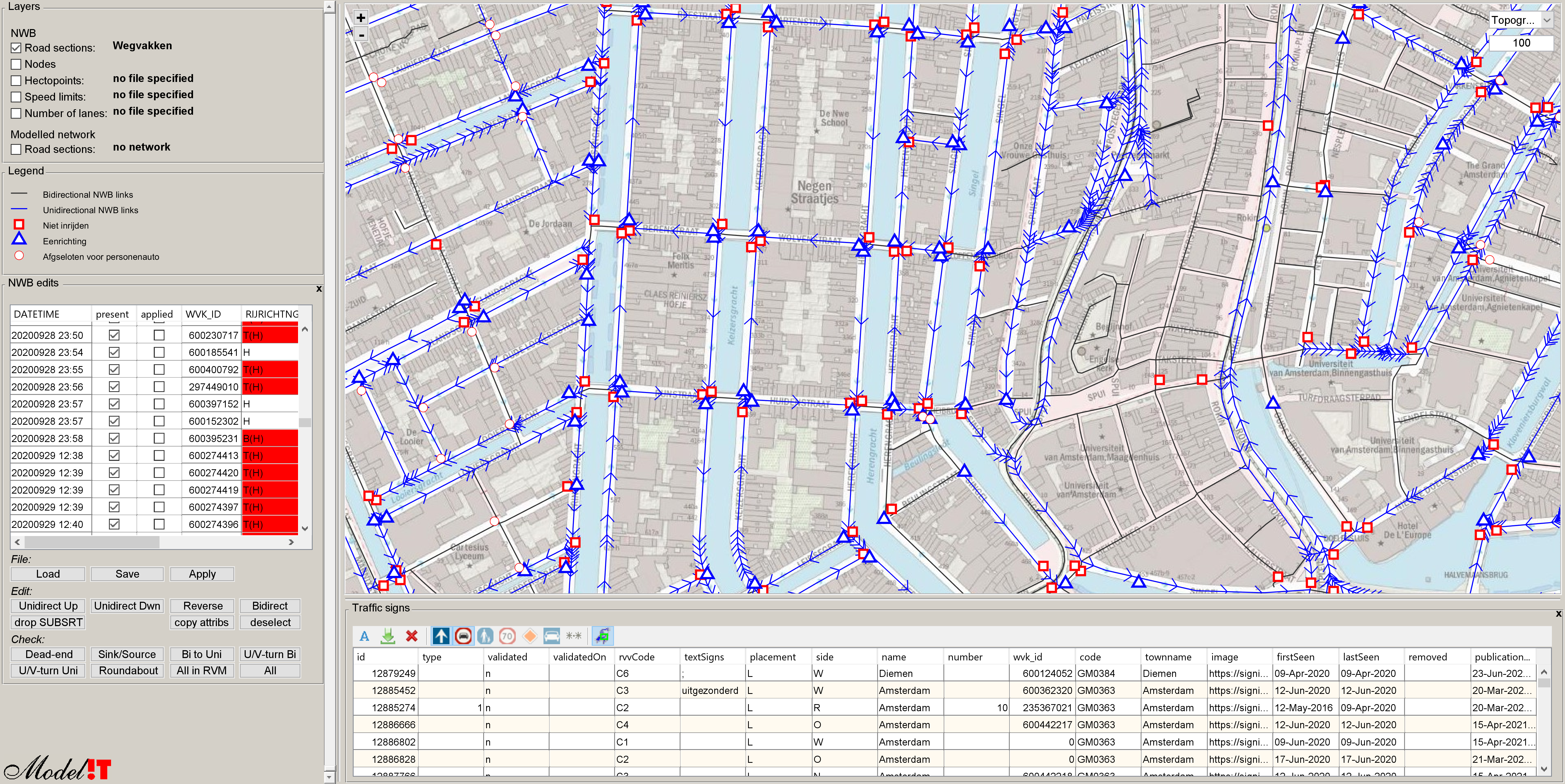
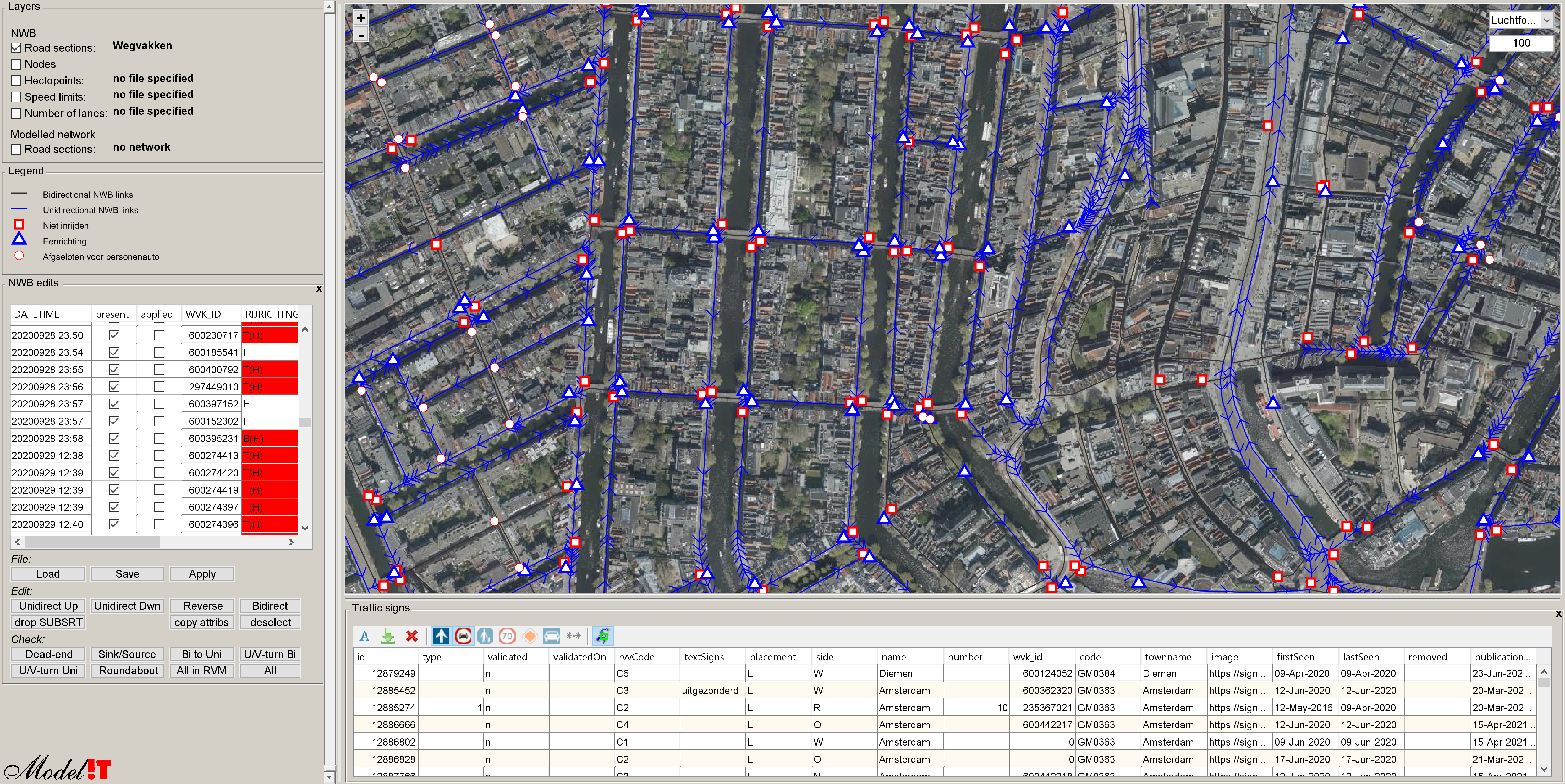
At Modelit we use the plugin during the process of creating a navigable map from the "Nationaal Wegen Bestand" (NWB). Although the topology of the map is very accurate occasional errors may occur. Especially with respect to allowed driving directions on the road sections that make up the network.
The correction process is a two stage process:
- step 1 automatically detects "suspicious" network layouts and marks them on the map. A typical suspicious local layout involves a sink- or source, forced u- or v- turns, or unexpected driving directions on roundabouts and intersections.
- step 2 involves a visual inspection which may or may not result in a mutation.
The visual inspection is aided by the display of areal photography and traffic signs. Mutations are added to a list that can be re-applied to each next version of the network. The list is also shared periodically with the creator of NWB.
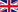
The image below shows implied traffic directions by "oneway" (blue) and "do not drive in" (red) signs
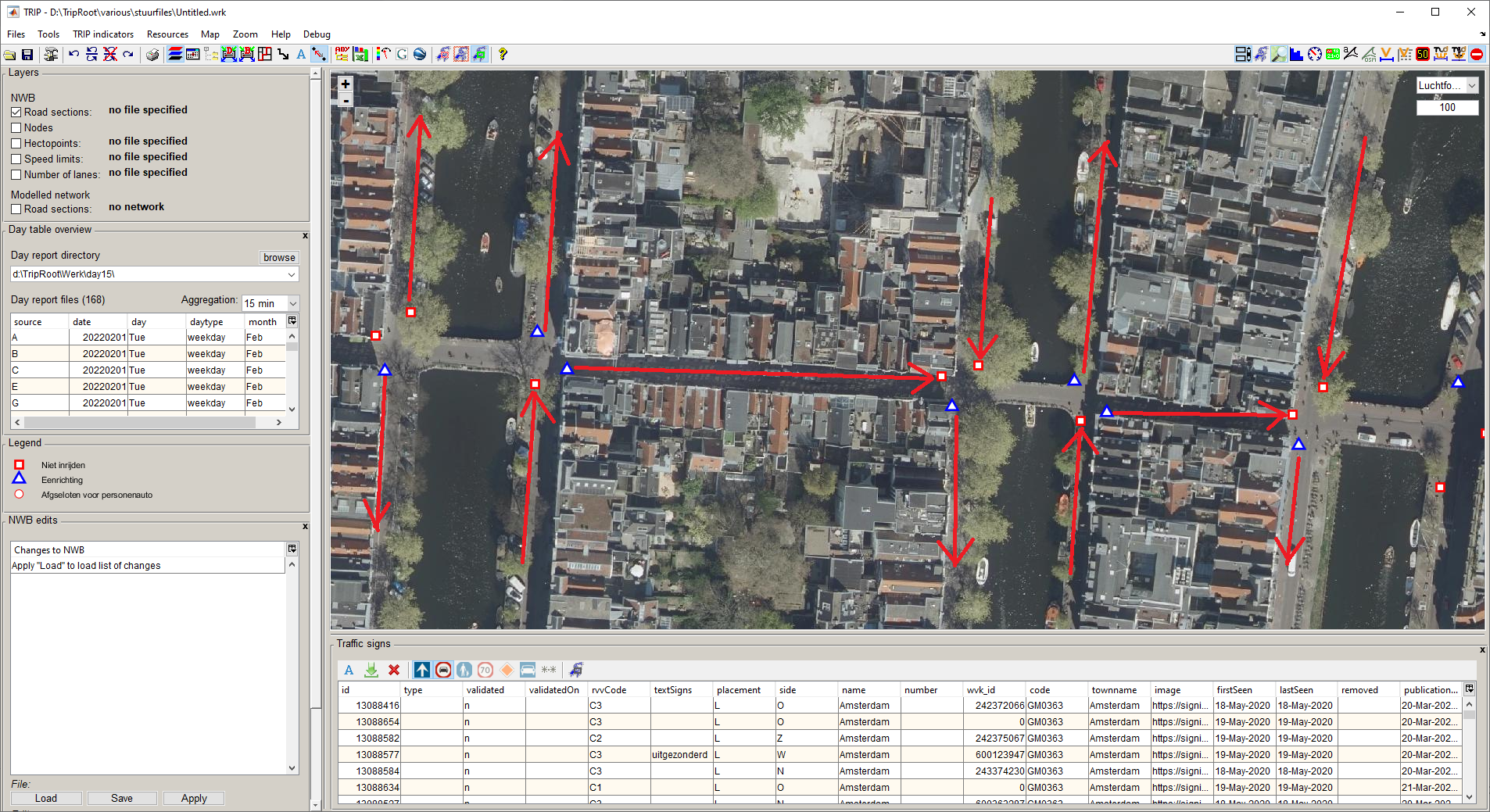
Network data can be verified visually by displaying different backgrounds
Areal photography is used for checking arrows on road surfaces and for recognition of typical layout patterns not shown on the map, such as intersections, roundabouts or traffic islands.
For ease of interpretation, layers can be "shaded"